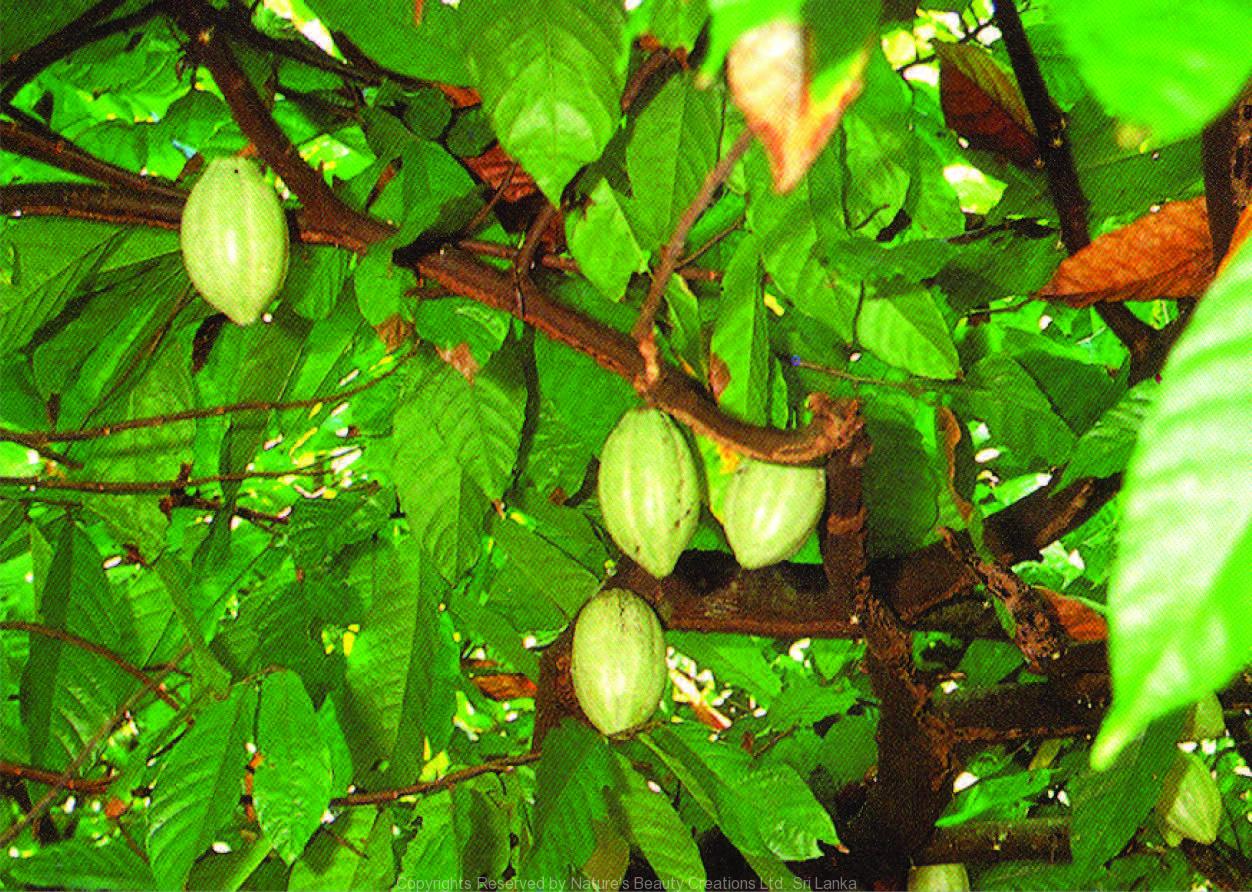

Traditional Knowledge
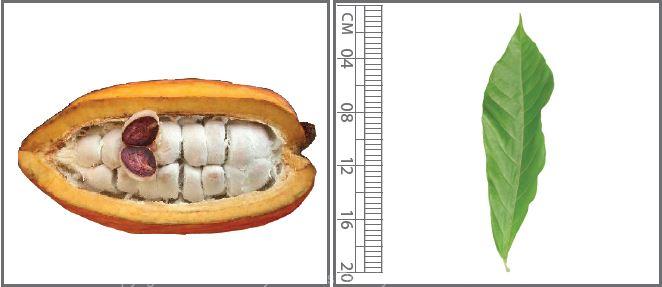
Useful plant parts :
Seed
Uses in traditional medicine :
- Possesses emollient properties and used to soften and treat dry skin and chapped lips
- A drink prepared from seeds act as a diuretic and given for fluid accumulation due to cardiac failure
- Used as a treatment for high blood pressure
Scientific Research
Chemical constituents:
Caffeolated amino acids: clovamide, deoxyclovamide and flavonoids: quercetin, its glucosides, epicatechin, procyanidins, proanthocyanidins and xanthine derivatives from beans and cocao liquor
Bioactivity :
Decoction of root: stabilizes red blood cells from stress injury; xanthine derivatives: protective effect against UV-induced wrinkle formation; polyphenols: antibacterial, anticariogenic, antioxidatixe, free radical scavenger, reduce biofilm formation and acid production by Streptococcus spp.; aqueous or ethanol extracts of bean powder: suppress pro-inflammatory pathways; flavonoids: antioxidative, protection and modulation of vascular homeostasis
Clinical:
Cocoa butter lipids exert a neutral cholesterolemic response
References : Bubonja-Sonje, M. et al., (2011), Antioxidant and antilisterial activity of olive oil, cocoa and rosemary extract polyphenols, Food Chemistry, 127, 1821–1827. Falade, O. S. et al., (2005), The chemical composition and membrane stability activity of some herbs used in local therapy for anemia, Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 102, 15–22. Ferrazzano, G. F. et al., (2009), Anti-cariogenic effects of polyphenols from plant stimulant beverages (cocoa, coffee, tea), Fitoterapia, 80, 255–262. Hatano, T. et al., (2002), Proanthocyanidin glycosides and related polyphenols from cacao liquor and their antioxidant effects, Phytochem- istry, 59, 749–758. Jenny, M. et al., (2009), Cacao extracts suppress tryptophan degradation of mitogen-stimulated peripheral blood mononuclear cells, Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 122, 261–267. Mitani, H. et al., (2007), Topical application of plant extracts containing xanthine derivatives can prevent UV-induced wrinkle formation in hairless mice, Photodermatology, Photoimmunology & Photomedicine, 23(2-3), 86–94. Mukherjee, P. K. et al., (2011), Bioactive compounds from natural resources against skin aging, Phytomedicine, 19, 64–73. Othman, A. et al. (2007), Antioxidant capacity and phenolic content of cocoa beans, Food Chemistry, 100, 1523–1530. Sanbongi, C. et al., (1998), Antioxidative Polyphenols Isolated from Theobroma cacao, Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 46(2), 454–457. Steinberg, F. M. et al., (2003), Cocoa and chocolate flavonoids: Implications for cardiovascular health, Journal of the American dietetic association, 103(2), 215-223.
Copyrights Reserved By
Natures Beauty Creations



